Overview
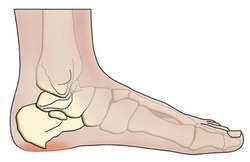
The heel spur (or calcaneal spur) is a nail-like growth of calcium around the ligaments and tendons of the foot where they attach to the heel bone. The spur grows from the bone and into the flesh of the foot.
A heel spur results from an anatomical change of the calcaneus (heel bone). This involves the area of the heel and commonly associated with plantar fasciitis.
The heel bone forms one end of the two longitudinal arches of the foot. These arches are held together by ligaments and are activated by the muscles of the foot (some of which are attached beneath the arches and run from the front to the back of the foot). These muscles and ligaments, like the other supporting tissues of the body, are attached in two places. Many are attached at the heel bone. The body reacts to the stress at the heel bone by calcifying the soft tissue attachments and creating a spur.
The heel spur (or calcaneal spur) is a nail-like growth of calcium around the ligaments and tendons of the foot where they attach to the heel bone. The spur grows from the bone and into the flesh of the foot.
A heel spur results from an anatomical change of the calcaneus (heel bone). This involves the area of the heel and commonly associated with plantar fasciitis.
The heel bone forms one end of the two longitudinal arches of the foot. These arches are held together by ligaments and are activated by the muscles of the foot (some of which are attached beneath the arches and run from the front to the back of the foot). These muscles and ligaments, like the other supporting tissues of the body, are attached in two places. Many are attached at the heel bone. The body reacts to the stress at the heel bone by calcifying the soft tissue attachments and creating a spur.
Symptoms
Although it may take years to become a problem, once it appears, it may cause considerable suffering. Because of proximity to the tendons, the spur is a source of continuous painful aching. The sensation has been described as "a toothache in the foot." When you place your weight on the heel, the pain can be sufficient to immobilize you.
The pain caused by a calcaneal spur is not the result of the pressure of weight on the point of the spur, but results from inflammation around the tendons where they attach to the heel bone. You might expect the pain to increase as you walk on the spur, but actually it decreases. The pain is most severe when you start to walk after a rest. The nerves and capillaries adapt themselves to the situation as you walk. When you rest, the nerves and capillaries rest, also. Then, as you begin to move about again, extreme demands are made on the blood vessels and nerves, which will cause pain until they again adjust to the spur.
If excessive strain has been placed on the foot the day before, the pain may also be greater. A sudden strain, as might be produced by leaping or jumping, can also increase the pain. The pain might be localized at first, but continued walking and standing will soon cause the entire heel to become tender and painful.
Treatment
The most effective treatment of heel spurs is custom orthotics with both a heel spur accommodation (horse-shoe shaped pad at the heel) and a heel cut out cushion accommodation. The idea is to take excess pressure off the center of the heel with the use of the heel spur accommodation and provide extra impact cushion with the use of the heel cut out cushion accommodation.
Although it may take years to become a problem, once it appears, it may cause considerable suffering. Because of proximity to the tendons, the spur is a source of continuous painful aching. The sensation has been described as "a toothache in the foot." When you place your weight on the heel, the pain can be sufficient to immobilize you.
The pain caused by a calcaneal spur is not the result of the pressure of weight on the point of the spur, but results from inflammation around the tendons where they attach to the heel bone. You might expect the pain to increase as you walk on the spur, but actually it decreases. The pain is most severe when you start to walk after a rest. The nerves and capillaries adapt themselves to the situation as you walk. When you rest, the nerves and capillaries rest, also. Then, as you begin to move about again, extreme demands are made on the blood vessels and nerves, which will cause pain until they again adjust to the spur.
If excessive strain has been placed on the foot the day before, the pain may also be greater. A sudden strain, as might be produced by leaping or jumping, can also increase the pain. The pain might be localized at first, but continued walking and standing will soon cause the entire heel to become tender and painful.
Treatment
The most effective treatment of heel spurs is custom orthotics with both a heel spur accommodation (horse-shoe shaped pad at the heel) and a heel cut out cushion accommodation. The idea is to take excess pressure off the center of the heel with the use of the heel spur accommodation and provide extra impact cushion with the use of the heel cut out cushion accommodation.

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
